Glaucoma is a degenerative eye disease that affects millions of people worldwide. This condition damages the optic nerve, leading to gradual vision loss if left untreated. However, with early detection and prevention, the effects of glaucoma can be mitigated. Regular eye tests are vital in identifying the disease in its early stages, allowing for timely medical intervention. In this article, we will explore the importance of eye tests for glaucoma and the various detection methods available to patients.
Understanding Glaucoma: A Brief Overview
To fully comprehend the significance of eye test for glaucoma, it is essential to have a basic understanding of this eye disease. Glaucoma typically occurs when there is a buildup of pressure inside the eye, causing damage to the optic nerve. This damage starts off subtly, often going unnoticed in its early stages. As the disease progresses, however, vision loss becomes more evident and irreversible. This is why early detection is crucial in preserving one’s eyesight.
By understanding the importance of early detection and prevention strategies, individuals can take proactive steps to combat glaucoma. Regular eye tests, healthy lifestyle choices, and timely treatment can make a significant difference in maintaining optimal eye health and preserving vision. Schedule your next eye exam today to ensure that you are taking the necessary steps to detect and prevent glaucoma at its earliest stages.
The Anatomy of the Eye and Glaucoma
Before delving into the specifics of glaucoma detection, it is important to briefly explore the anatomy of the eye. The eye is a complex organ with various components working together to facilitate vision. The optic nerve, in particular, connects the eye to the brain, allowing visual information to be processed. Glaucoma directly targets this vital nerve, leading to vision impairment.
Furthermore, within the eye, there is a delicate balance of fluid production and drainage. When this balance is disrupted, as seen in glaucoma, the pressure inside the eye can increase, causing damage to the optic nerve. The trabecular meshwork, a tiny sieve-like drainage system located near the front of the eye, plays a crucial role in regulating this fluid balance. Dysfunction in this area can contribute to the development of glaucoma.
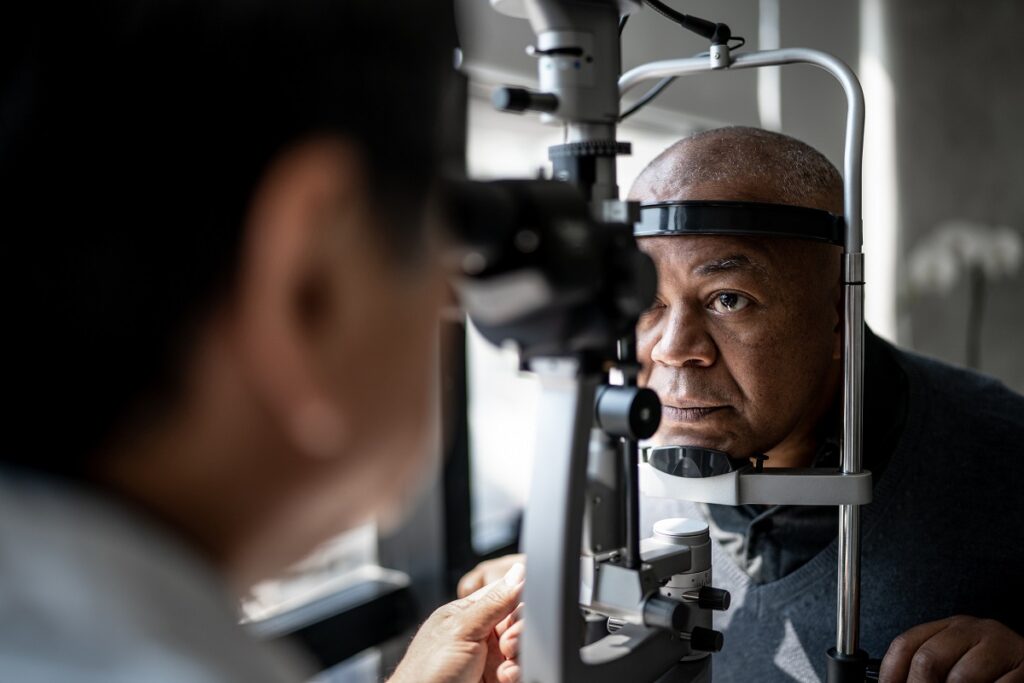
Types of Glaucoma
There are several types of glaucoma, each with its own distinct characteristics. The most common form is primary open-angle glaucoma, which tends to develop slowly over time. Angle-closure glaucoma, on the other hand, occurs when the drainage angle of the eye becomes blocked suddenly, resulting in a rapid increase in eye pressure. Other forms of glaucoma include normal-tension glaucoma and secondary glaucoma, which can be caused by certain medical conditions or eye injuries.
It is important to note that while primary open-angle glaucoma is the most prevalent type, angle-closure glaucoma is considered a medical emergency due to its rapid onset and potential for severe vision loss. Understanding the different types of glaucoma is crucial for healthcare providers to accurately diagnose and manage the condition in patients of varying risk factors and symptoms.
Know about causes of glucoma at: Common Causes of Glaucoma and How to Manage Symptoms
The Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of glaucoma is essential as it allows for prompt intervention, reducing the risk of irreversible vision loss. Without regular eye tests, this degenerative disease can progress silently, making it difficult to detect until significant damage has occurred.
Regular eye examinations are crucial for individuals of all ages, as glaucoma can affect anyone, regardless of their visual acuity. By detecting glaucoma early, not only can vision loss be prevented, but overall eye health can be maintained for a better quality of life. It is recommended to schedule comprehensive eye exams at least once a year to monitor any changes in eye health and address any potential issues promptly.
Progression of Glaucoma
Glaucoma typically progresses slowly, gradually impairing vision over time. In the early stages, individuals may not experience any noticeable symptoms, making it imperative to undergo regular eye tests. By monitoring changes in eye pressure, optic nerve health, and visual field, optometrists can catch glaucoma at its earliest stages.
Furthermore, advancements in technology have improved the early detection methods for glaucoma. From specialized imaging techniques to innovative diagnostic tools, optometrists now have a wide array of resources to detect glaucoma in its initial phases. This early detection not only helps in preserving vision but also aids in developing personalized treatment plans for each patient based on their specific needs and risk factors. Read more about risk at https://www.marquette.edu/riskunit/riskmanagement/whatis.shtml
Risks of Late Detection
If glaucoma is not detected early on, it can lead to severe visual impairment, possibly resulting in blindness. Timely detection allows for treatment to begin before irreversible damage occurs. Additionally, late-stage glaucoma requires more aggressive treatment methods, potentially leading to higher costs and increased discomfort for the patient.
It is important for individuals to be proactive about their eye health and not wait for symptoms to appear before seeking an eye exam. By prioritizing regular check-ups and early detection, the risks associated with glaucoma can be minimized, ensuring long-term eye health and visual acuity.
Eye Tests for Glaucoma
When it comes to detecting glaucoma, there are several eye tests available that can provide comprehensive information about the condition. These tests analyze different aspects of the eye, allowing optometrists to diagnose and monitor the disease effectively.
Comprehensive Eye Exam
A comprehensive eye exam serves as the foundation for glaucoma detection. During this examination, optometrists conduct a thorough evaluation of the eye’s structure and function. They measure eye pressure, assess visual acuity, and carefully examine the optic nerve. By assessing these factors, optometrists can identify potential signs of glaucoma and determine the best course of action.
Tonometry: Measuring Eye Pressure
Tonometry is a crucial test that measures the pressure inside the eye. Elevated eye pressure is a common sign of glaucoma, making this test instrumental in its detection. There are different tonometry methods available, including the use of a specialized instrument or a gentle puff of air directed onto the eye’s surface. By accurately measuring eye pressure, optometrists can assess the risk of glaucoma and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Perimetry: Visual Field Test
A perimetry test plays a vital role in identifying glaucoma by measuring the full extent of an individual’s field of vision. This test helps detect any areas of vision loss, which could indicate the presence of glaucoma. By conducting regular perimetry tests, optometrists can track changes in peripheral vision over time, allowing for prompt intervention and management of the disease.
Gonioscopy: Examining the Drainage Angle
Gonioscopy is a specialized examination that focuses on the drainage angle of the eye. Using a contact lens with a mirrored surface, optometrists can visualize the angle and assess potential blockages that may contribute to an increase in eye pressure. By carefully examining the drainage angle, optometrists can gain valuable insights into the underlying causes of glaucoma and develop targeted treatment strategies. Click here to learn more about pressure.
Pachymetry: Corneal Thickness Measurement
Pachymetry is a test that measures the thickness of the cornea, the clear front surface of the eye. Research has shown that thinner corneas are associated with an increased risk of glaucoma. By evaluating corneal thickness, optometrists can better understand a patient’s overall glaucoma risk and tailor their approach accordingly. This information helps in determining the most suitable treatment options and monitoring the progression of the disease.
These eye tests, combined with the expertise of optometrists, play a crucial role in the early detection and management of glaucoma. Regular screenings and comprehensive evaluations are essential for preserving vision and maintaining eye health. If you have any concerns or questions about glaucoma, it is always recommended to consult with an eye care professional who can provide personalized guidance and care.
Prevention Strategies for Glaucoma
While early detection is crucial, preventive strategies can also play a significant role in reducing the risk of developing glaucoma.
Glaucoma is a progressive eye condition that can lead to irreversible vision loss if left untreated. In addition to regular eye check-ups and early detection, there are several lifestyle modifications and treatment options that can help prevent the advancement of the disease.
Regular Eye Check-ups
Scheduling regular eye check-ups with an optometrist is essential in maintaining optimal eye health. Routine examinations allow for the early detection of glaucoma or other eye conditions, ensuring swift intervention and timely treatment.
During an eye exam, the optometrist may perform various tests to assess the intraocular pressure, examine the optic nerve, and evaluate the visual field. These tests are crucial in detecting glaucoma in its early stages when treatment is most effective.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Engaging in a healthy lifestyle can contribute to the prevention of glaucoma. Regular exercise, a balanced diet rich in antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids, and avoidance of smoking can promote overall well-being, reduce intraocular pressure, and decrease the risk of developing various health conditions, including glaucoma.
In addition to lifestyle modifications, incorporating foods high in vitamin C, vitamin E, zinc, and beta-carotene can provide essential nutrients for maintaining eye health and potentially slowing the progression of glaucoma.
Medication and Treatment Options
For individuals diagnosed with glaucoma, a range of medication and treatment options are available. Eye drops, oral medications to reduce intraocular pressure, laser procedures to improve fluid drainage, and even surgical interventions may be recommended to manage the disease and prevent further damage to the optic nerve.
It is important for individuals with glaucoma to adhere to their prescribed treatment plan, attend regular follow-up appointments, and communicate any changes in their vision or symptoms to their eye care provider promptly.

