Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder that can cause daytime fatigue and irritability if it keeps you up at night. It can also lead to weight gain, hypertension, and an increased risk of diabetes. Petoskey Ear, Nose & Throat Specialists in Petoskey, Gaylord, and St. Ignace, Michigan, can help treat sleep apnea.
There are two types of sleep apnea: Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) and Central Sleep Apnea (CSA). Sleep apnea solutions include Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP). People with mild, moderate, and severe OSA may benefit from a sleep study by a sleep specialist to determine the best treatment.
What is sleep apnea?
Millions of Americans have mild obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), a common sleep disorder. OSA occurs when muscles in the throat, soft palate, tonsils, and tongue relax too much when you fall asleep, narrowing airways and preventing you from getting enough air as you inhale. Low blood oxygen levels can cause you to wake up briefly and take a deep breath.
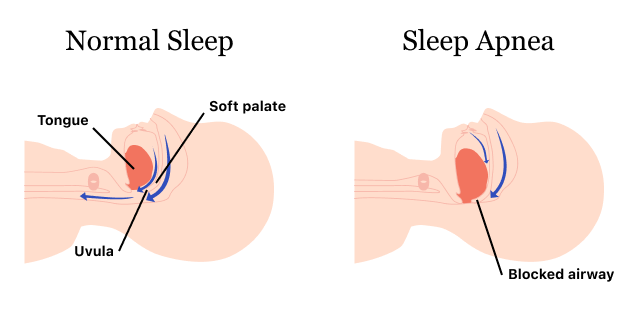
People don’t remember these episodes because they’re brief, but they can happen many times each hour. Risk factors for sleep apnea include loud snoring, high blood pressure, and being overweight. If left untreated, sleep apnea can lead to heart disease, stroke, and other health problems. sleep apnea solutions, such as CPAP, is often used to treat OSA. In some cases, treatment-emergent central sleep apnea is used to diagnose and treat sleep-disordered breathing.
See Also: How to Pick the Best CPAP Machine Battery Solutions
Healthy sleep is important
Healthy sleep is important for keeping blood oxygen levels normal and reducing high blood pressure. Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) is the most common type of sleep apnea, which can be treated with oral appliances, clinical sleep medicine, sleeping pills, and losing weight. Central Sleep Apnea (CSA) is less common than OSA and is caused when the brain does not send signals to the muscles that control breathing. How is sleep apnea prevented?
The upper airway, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, and chronic lung diseases are all risk factors for sleep apnea. Daytime fatigue, falling asleep and oxygen levels can be improved with Bilevel Positive Airway Pressure (BPAP). Losing weight and avoiding alcohol can also help to prevent sleep apnea.
Sleep apnea is a disorder where a person’s breathing stops and starts during sleep. Symptoms of sleep apnea, such as loud snoring, gasping for breath and pauses in breathing that can wake the person, their partner, and anyone else in the household, can lead to unhealthy sleep patterns. To prevent sleep apnea, losing weight, avoiding sleeping pills, and using oral appliances can help.
Clinical sleep medicine can also provide bilevel-positive airway pressure and other treatments. Central sleep apnea (CSA) and obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) can both cause high blood pressure, daytime fatigue, and lower oxygen levels in the blood. How is sleep apnea treated? Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, chronic lung diseases, and other conditions can increase the risk of sleep apnea. The upper airway needs to remain open during sleep to help prevent sleep apnea from happening.
What are the daytime symptoms of sleep apnea?
Daytime symptoms of OSA include:
- Fatigue
- Excessive daytime sleepiness
- Difficulty concentrating
- Drops in motivation
- Irritability
- Headaches, typically in the morning
- Excessively dry mouth in the morning
- Depression and anxiety
- Increased incidence of work-related accidents
- Problems completing work or school tasks
Sleep apnea is a serious sleep disorder where your airway partially or completely collapses during sleep, leading to loud snoring and disturbed breathing.
Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder that can cause low oxygen levels in the blood, resulting in restless sleep and trouble concentrating. Obstructive sleep apnea and central sleep apnea are two types of this disorder. To treat sleep apnea, people may use oral appliances, other airway pressure devices, or weight loss.
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) is also used to widen the airway and relax the upper airway muscles. People with mild, moderate, or severe obstructive sleep apnea, central sleep apnea, or obstructive sleep apnea syndrome should seek help from a sleep specialist to treat their sleep disorder. A sleep study may also be recommended. Treatment may help reduce daytime sleepiness.
Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder. OSA and CSA are two types. People with severe OSA need to consult a specialist. CPAP can treat mild to moderate OSA. Severe cases may need a sleep study. Symptoms like snoring and sleepiness are reduced with CPAP. Treatment can improve breathing and oxygen levels.
However, lack of normal sleep can still cause metabolic syndrome, increased risk of atrial fibrillation, and other health risks.
What are the health complications of sleep apnea?
Left untreated, lowered blood oxygen (hypoxia), changes in carbon dioxide levels, and the resulting inflammatory response associated with sleep apnea increase your risk of:
- Heart disease
- Stroke
- Treatment-resistant hypertension
- Diabetes
- Enlarged heart (cardiomyopathy)
- Heart attack
- Irregular heart rate (arrhythmia)
- Heart failure
Sleep Apnea is a sleep disorder and can be classified into three types: Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA), Central Sleep Apnea (CSA), and Complex Sleep Apnea Syndrome. People with OSA have airway blockage, resulting in severe health risks.
A Sleep Specialist can provide an accurate diagnosis and recommend effective treatments including Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) to keep the airways open and restore restful sleep. Treating Sleep Apnea can help reduce the risks associated with mild, moderate, and severe Sleep Apnea. A Sleep Study may be required to assess the level of Daytime Sleepiness.
How do you treat sleep apnea?
People with sleep apnea have narrowed airways, causing loud snoring and restless sleep. This can lead to decreased breathing and oxygen levels, resulting in frequent changes in blood oxygen levels. Symptoms like lack of sleep, trouble concentrating, and daytime sleepiness can occur.
Treatments for sleep apnea come in various forms, such as continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP), sleep specialist, and sleep study. Sleep disorders can be mild, moderate, or severe, and can manifest as obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), central sleep apnea (CSA), or obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS). Treatment for these sleep disorders can vary from mild to severe.
To address this, an oral appliance, other airway pressure devices, or even weight loss may be suggested to help strengthen the throat muscles. Metabolic syndrome, atrial fibrillation, and other sleep disorders may also increase risk. Soft palate, upper airway muscles, and emergent central sleep apnea can be treated with these devices to help restore normal sleep and breathing and oxygen levels.
Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder that can cause daytime sleepiness. It can be mild, moderate, or severe. Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and central sleep apnea (CSA) are the two main types. Treatment of OSA includes a customized oral appliance that shifts the jaw forward slightly while sleeping to prevent throat muscles from collapsing and blocking airways.
Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) is used to treat both OSA and CSA. People with sleep apnea should see a sleep specialist for evaluation and treatment. A sleep study may be recommended.

